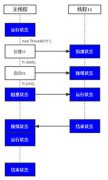
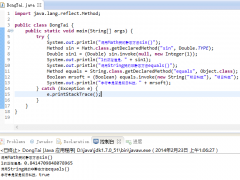
Java运算符总结
运算符总结 下面这个例子向大家展示了如何随同特定的运算符使用主数据类型。从根本上说,它是同一个例子反反复复地执行,只是使用了不同的主数据类型。文件编译时不会报错,因
运算符总结
下面这个例子向大家展示了如何随同特定的运算符使用主数据类型。从根本上说,它是同一个例子反反复复地执行,只是使用了不同的主数据类型。文件编译时不会报错,因为那些会导致错误的行已用//!变成了注释内容。
//: AllOps.Java
// Tests all the operators on all the
// primitive data types to show which
// ones are accepted by the Java compiler.
class AllOps {
// To accept the results of a boolean test:
void f(boolean b) {}
void boolTest(boolean x, boolean y) {
// Arithmetic operators:
//! x = x * y;
//! x = x / y;
//! x = x % y;
//! x = x + y;
//! x = x - y;
//! x++;
//! x--;
//! x = +y;
//! x = -y;
// Relational and logical:
//! f(x > y);
//! f(x >= y);
//! f(x < y);
//! f(x < = y);
f(x == y);
f(x != y);
f(!y);
x = x && y;
x = x y;
// Bitwise operators:
//! x = ~y;
x = x & y;
x = x y;
x = x ^ y;
//! x = x < < 1;
//! x = x >> 1;
//! x = x >>> 1;
// Compound assignment:
//! x += y;
//! x -= y;
//! x *= y;
//! x /= y;
//! x %= y;
//! x < < = 1;
//! x >>= 1;
//! x >>>= 1;
x &= y;
x ^= y;
x = y;
// Casting:
//! char c = (char)x;
//! byte B = (byte)x;
//! short s = (short)x;
//! int i = (int)x;
//! long l = (long)x;
//! float f = (float)x;
//! double d = (double)x;
}
void charTest(char x, char y) {
// Arithmetic operators:
x = (char)(x * y);
x = (char)(x / y);
x = (char)(x % y);
x = (char)(x + y);
x = (char)(x - y);
x++;
x--;
x = (char)+y;
x = (char)-y;
// Relational and logical:
f(x > y);
f(x >= y);
f(x < y);
f(x < = y);
f(x == y);
f(x != y);
//! f(!x);
//! f(x && y);
//! f(x y);
// Bitwise operators:
x= (char)~y;
x = (char)(x & y);
x = (char)(x y);
x = (char)(x ^ y);
x = (char)(x < < 1);
x = (char)(x >> 1);
x = (char)(x >>> 1);
// Compound assignment:
x += y;
x -= y;
x *= y;
x /= y;
x %= y;
x < < = 1;
x >>= 1;
x >>>= 1;
x &= y;
x ^= y;
x = y;
// Casting:
//! boolean b = (boolean)x;
byte B = (byte)x;
short s = (short)x;
int i = (int)x;
long l = (long)x;
float f = (float)x;
double d = (double)x;
}
void byteTest(byte x, byte y) {
// Arithmetic operators:
x = (byte)(x* y);
x = (byte)(x / y);
x = (byte)(x % y);
x = (byte)(x + y);
x = (byte)(x - y);
x++;
x--;
x = (byte)+ y;
x = (byte)- y;
// Relational and logical:
f(x > y);
f(x >= y);
f(x < y);
f(x < = y);
f(x == y);
f(x != y);
//! f(!x);
//! f(x && y);
//! f(x y);
// Bitwise operators:
x = (byte)~y;
x = (byte)(x & y);
x = (byte)(x y);
x = (byte)(x ^ y);
x = (byte)(x < < 1);
x = (byte)(x >> 1);
x = (byte)(x >>> 1);
// Compound assignment:
x += y;
x -= y;
x *= y;
x /= y;
x %= y;
x < < = 1;
x >>= 1;
x >>>= 1;
x &= y;
x ^= y;
x = y;
// Casting:
//! boolean b = (boolean)x;
char c = (char)x;
short s = (short)x;
int i = (int)x;
long l = (long)x;
float f = (float)x;
double d = (double)x;
}
void shortTest(short x, short y) {
// Arithmetic operators:
x = (short)(x * y);
x = (short)(x / y);
x = (short)(x % y);
x = (short)(x + y);
x = (short)(x - y);
x++;
x--;
x = (short)+y;
x = (short)-y;
// Relational and logical:
f(x > y);
f(x >= y);
f(x < y);
f(x < = y);
f(x == y);
f(x != y);
//! f(!x);
//! f(x && y);
//! f(x y);
// Bitwise operators:
x = (short)~y;
x = (short)(x & y);
x = (short)(x y);
x = (short)(x ^ y);
x = (short)(x < < 1);
x = (short)(x >> 1);
x = (short)(x >>> 1);
// Compound assignment:
x += y;
x -= y;
x *= y;
x /= y;
x %= y;
x < < = 1;
x >>= 1;
x >>>= 1;
x &= y;
x ^= y;
x = y;
// Casting:
//! boolean b = (boolean)x;
char c = (char)x;
byte B = (byte)x;
int i = (int)x;
long l = (long)x;
float f = (float)x;
double d = (double)x;
}
void intTest(int x, int y) {
// Arithmetic operators:
x = x * y;
x = x / y;
x = x % y;
x = x + y;
x = x - y;
x++;
x--;
x = +y;
x = -y;
// Relational and logical:
f(x > y);
f(x >= y);
f(x < y);
f(x < = y);
f(x == y);
f(x != y);
//! f(!x);
//! f(x && y);
//! f(x y);
// Bitwise operators:
x = ~y;
x = x & y;
x = x y;
x = x ^ y;
x = x < < 1;
x = x >> 1;
x = x >>> 1;
// Compound assignment:
x += y;
x -= y;
x *= y;
x /= y;
x %= y;
x < < = 1;
x >>= 1;
x >>>= 1;
x &= y;
x ^= y;
x = y;
// Casting:
//! boolean b = (boolean)x;
char c = (char)x;
byte B = (byte)x;
short s = (short)x;
long l = (long)x;
float f = (float)x;
double d = (double)x;
}
void longTest(long x, long y) {
// Arithmetic operators:
x = x * y;
x = x / y;
x = x % y;
x = x + y;
x = x - y;
x++;
x--;
x = +y;
x = -y;
// Relational and logical:
f(x > y);
f(x >= y);
f(x < y);
f(x < = y);
f(x == y);
f(x != y);
//! f(!x);
//! f(x && y);
//! f(x y);
// Bitwise operators:
x = ~y;
x = x & y;
x = x y;
x = x ^ y;
x = x < < 1;
x = x >> 1;
x = x >>> 1;
// Compound assignment:
x += y;
x -= y;
x *= y;
x /= y;
x %= y;
x < < = 1;
x >>= 1;
x >>>= 1;
x &= y;
x ^= y;
x = y;
// Casting:
//!
精彩图集
精彩文章