Java多线程同步中的两个特殊类
Java语言内置了synchronized要害字用于对多线程进行同步,大大方便了Java中多线程程序的编写。但是仅仅使用synchronized要害字还不能满足对多线程进行同步的所有需要。大家知道,synchro
Java语言内置了synchronized要害字用于对多线程进行同步,大大方便了Java中多线程程序的编写。但是仅仅使用synchronized要害字还不能满足对多线程进行同步的所有需要。大家知道,synchronized仅仅能够对方法或者代码块进行同步,假如我们一个应用需要跨越多个方法进行同步,synchroinzed就不能胜任了。在C++中有很多同步机制,比如信号量、互斥体、临届区等。在Java中也可以在synchronized语言特性的基础上,在更高层次构建这样的同步工具,以方便我们的使用。
当前,广为使用的是由Doug Lea编写的一个Java中同步的工具包,可以在这儿了解更多这个包的具体情况:
http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/classes/EDU/oswego/cs/dl/util/concurrent/intro.Html
该工具包已经作为JSR166正处于JCP的控制下,即将作为JDK1.5的正式组成部分。本文并不打算具体剖析这个工具包,而是对多种同步机制的一个介绍,同时给出这类同步机制的实例实现,这并不是工业级的实现。但其中会参考Doug Lea的这个同步包中的工业级实现的一些代码片断。
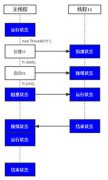
本例中还沿用上篇中的Account类,不过我们这儿编写一个新的ATM类来模拟自动提款机,通过一个ATMTester的类,生成10个ATM线程,同时对John账户进行查询、提款和存款操作。Account类做了一些改动,以便适应本篇的需要:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Account
{
String name;
//float amount;
//使用一个Map模拟持久存储
static Map storage = new HashMap();
static
{
storage.put("John", new Float(1000.0f));
storage.put("Mike", new Float(800.0f));
}
public Account(String name)
{
//System.out.println("new account:" + name);
this.name = name;
//this.amount = ((Float)storage.get(name)).floatValue();
}
public synchronized void deposit(float amt)
{
float amount = ((Float)storage.get(name)).floatValue();
storage.put(name, new Float(amount + amt));
}
public synchronized void withdraw(float amt)
throws InsufficientBalanceException
{
float amount = ((Float)storage.get(name)).floatValue();
if (amount >= amt) amount -= amt;
else throw new InsufficientBalanceException();
storage.put(name, new Float(amount));
}
public float getBalance()
{
float amount = ((Float)storage.get(name)).floatValue();
return amount;
}
}
在新的Account类中,我们采用一个HashMap来存储账户信息。Account由ATM类通过login登录后使用:
public class ATM
{
Account acc;
//作为演示,省略了密码验证
public boolean login(String name)
{
if (acc != null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Already logged in!");
acc = new Account(name);
return true;
}
public void deposit(float amt)
{
acc.deposit(amt);
}
public void withdraw(float amt) throws InsufficientBalanceException
{
acc.withdraw(amt);
}
public float getBalance()
{
return acc.getBalance();
}
public void logout ()
{
acc = null;
}
}
下面是ATMTester,在ATMTester中首先生成了10个ATM实例,然后启动10个线程,同时登录John的账户,先查询余额,然后,再提取余额的80%,然后再存入等额的款(以维持最终的余额的不变)。按照我们的预想,应该不会发生金额不足的问题。首先看代码:
public class ATMTester
{
private static final int NUM_OF_ATM = 10;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ATMTester tester = new ATMTester();
final Thread thread[] = new Thread[NUM_OF_ATM];
final ATM atm[] = new ATM[NUM_OF_ATM];
for (int i=0; i<NUM_OF_ATM; i++)
{
atm[i] = new ATM();
thread[i] = new Thread(tester.new Runner(atm[i]));
thread[i].start();
}
}
class Runner implements Runnable
{
ATM atm;
Runner(ATM atm)
{
this.atm = atm;
}
public void run()
{
atm.login("John");
//查询余额
float bal = atm.getBalance();
try
{
Thread.sleep(1);
//模拟人从查询到取款之间的间隔
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{ // ignore it }
try
{
System.out.println("Your balance is:" + bal);
System.out.println("withdraw:" + bal * 0.8f);
atm.withdraw(bal * 0.8f);
System.out.println("deposit:" + bal * 0.8f);
atm.deposit(bal * 0.8f);
}
catch (InsufficientBalanceException e1)
{
System.out.println("余额不足!");
}
finally
{ atm.logout(); }
}
}
}
运行ATMTester,结果如下(每次运行结果都有所差异):
Your balance is:1000.0
withdraw:800.0
deposit:800.0
Your balance is:1000.0
Your balance is:1000.0
withdraw:800.0
withdraw:800.0
余额不足!
Your balance is:200.0
Your balance is:200.0
Your balance is:200.0
余额不足!
Your balance is:200.0
Your balance is:200.0
Your balance is:200.0
Your balance is:200.0
withdraw:160.0
withdraw:160.0
withdraw:160.0
withdraw:160.0
withdraw:160.0
withdraw:160.0
withdraw:160.0
deposit:160.0
余额不足!
余额不足!
余额不足!
余额不足!
余额不足!
余额不足!
为什么会出现这样的情况?因为我们这儿是多个ATM同时对同一账户进行操作,比如一个ATM查询出了余额为1000,第二个ATM也查询出了余额1000,然后两者都期望提取出800,那么只有第1个用户能够成功提出,因为在第1个提出800后,账户真实的余额就只有200了,而第二个用户仍认为余额为1000。这个问题是由于多个ATM同时对同一个账户进行操作所不可避免产生的后果。要解决这个问题,就必须限制同一个账户在某一时刻,只能由一个ATM进行操作。如何才能做到这一点?直接通过synchronized要害字可以吗?非常遗憾!因为我们现在需要对整个Account的多个方法进行同步,这是跨越多个方法的,而synchronized仅能对方法或者代码块进行同步。 QQRead.com 推出数据恢复指南教程 数据恢复指南教程 数据恢复故障解析 常用数据恢复方案 硬盘数据恢复教程 数据保护方法 数据恢复软件 专业数据恢复服务指南
我们首先开发一个BusyFlag的类,类似于C++中的Simaphore。
public class BusyFlag
{
protected Thread busyflag = null;
protected int busycount = 0;
public synchronized void getBusyFlag()
{
while (tryGetBusyFlag() == false)
{
try
{
wait();
}
catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
private synchronized boolean tryGetBusyFlag()
{
if (busyflag == null)
{
busyflag = Thread.currentThread();
busycount = 1;
return true;
}
if (busyflag == Thread.currentThread())
{
busycount++; return true;
}
return false;
}
public synchronized void freeBusyFlag()
{
if(getOwner()== Thread.currentThread())
{
busycount--;
if(busycount==0)
{
busyflag = null;
notify();
}
}
}
public synchronized Thread getOwner()
{
return busyflag;
}
}
精彩图集
精彩文章