Java中利用管道实现线程间的通讯
作者:jianada 来源 emook 在Java 语言中,提供了各种各样的输入输出流(stream),使我们能够很方便的对数据进行操作,其中,管道(pipe)流是一种非凡的流,用于在不同线程(threads)间
作者:jianada 来源 emook
在Java 语言中,提供了各种各样的输入输出流(stream),使我们能够很方便的对数据进行操作,其中,管道(pipe)流是一种非凡的流,用于在不同线程(threads)间直接传送数据。一个线程发送数据到输出管道,另一个线程从输入管道中读数据。通过使用管道,实现不同线程间的通讯。无需求助于类似临时文件之类的东西。本文在简要介绍管道的基本概念后,将以一个具体的实例pipeapp加以具体说明。
1. 管道的创建与使用
java提供了两个非凡的专门的类专门用于处理管道,它们就是pipedinputstream类和pipeoutputstream类。
Pipedinputstream代表了数据在管道中的输出端,也就是线程向管道读数据的一端;pipeoutputstream代表了数据在管道中的输入端,也就是线程向管道写数据的一端,这两个类一起使用可以提供数据的管道流。
为了创建一个管道流,我们必须首先创建一个pipeoutstream对象,然后,创建pipeinputstream对象,实例如下:
pipeout= new pipedyoutstream();
pipein= new pipedputsteam(pipepout);
一旦创建了一个管道后,就可以象操作文件一样对管道进行数据的读写。
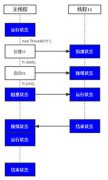
2. 演示程序: pipeapp
应用程序由三个程序组成:主线程(pipeapp.java)及由主线程启动的两个二级线程(ythread.java和zthread.java),它们使用管道来处理数据。程序从一个内容为一行一行"x"字母的"input.txt"文件中读取数据,使用管道传输数据,第一次是利用线程ythread将数据"x"转换为"y",最后利用线程zthread将"y"转换为"z",之后,程序在屏幕上显示修改后的数据。
主线程 (pipeapp.java)
在main()方法中,程序首先创建一个应用对象:pipeapp pipeapp=new pipeapp();
由于程序中流操作都需要使用IOException异常处理,所以设置了一个try块。在try中,为了从源文件中读取数据,程序为"input.txt"文件创建了一个输入流Xfileln,:
fileinputstream xfileln= new fileinputstream("input.txt");
新的输入流传递给changetoy()方法,让线程ythread能读取该文件:
inputstream ylnpipe =pipeapp.changetoy(xfileln);
changetoy()方法创建将输入数据"x"改变到"y"的线程ythread,并返回该线程的输入管道:
inputstream zlnpipe = pipeapp.changetoz(ylnpipe);
changetoz()方法启动将数据从"y"改变到"z"的线程zehread,主程序将使用从changetoz()返回的输入管道。得到以修改的数据。
然后,程序将管道输入流定位到datainputstream对象,使程序能够使用readline()方法读取数据:
datainputstream inputstream = new datainputstream(zlnpiepe);
创建了输入流以后,程序就可以以行一行的读取数据病显示在屏幕上。
String str= inputstream.readline();
While(str!=null)
{
system.out.println(str);
str=inputstream.readline();
}
显示完成之后,程序关闭输入流:
inputstream.close();
changetoy()方法
changetoy()方法首先通过传递一个参数inputstream给datainputstream对象来定位资源的输入流,使程序能使用readline()方法从流中读取数据:
datainputstream xfileln =new datainutstream(inputstream);
然后,changetoy()创建输出管道和输入管道:
pipeoutstream pipeout = new pipeoutputstream();
pipeinputstream pipeln = new pipedinputsteam(pipeout);
为了能够使用println()方法输出修改的后的文本行到管道,程序将输出管道定位到printstream对象:
printstream printstream = new printstream(pipeout);
现在,程序可以创建将数据从x改变到y的线程,该线程是ythread类的一个对象,他传递两个参数:输入文件(xfileln)和输出管道(调用printstream)
ythread ythread =new thread(xfileln,printstream);
之后,程序启动线程:
changetoz()方法
changetoz()方法与changetoy()方法很相似,他从changetoy()返回的输入流开始:
datainputstream yfileln= new datainputstream(inputstream);
程序创建一个新的管道:
pipedoutstream pipeout2 = new pipedoutputstream();
pipedinputstream pipeln2 = new pipedinputsream(pipeout2);
该线程通过这个新的管道发出修改后的数据(输入流pipeln2)给主程序。
源程序如下:
//
//pipeapp.java-pipeapp的主应用程序
//
import java.io.*
class pipeapp
{
public static void main(string[] args)
{
pipeapp pipeapp=new pipeapp();
try
{
fileinputstream xfile =new fileinputstream("input.txt");
inputstream ylnpipe = pipeapp.changetoy(xfileln);
inputstream zlnpipe=pipeapp.changetoz(ylnpipe);
system.out.println();
system.out.println("here are the results");
system.out.pringln();
datainputstream inputstream = nes datainputstream(zlnpipe);
string str = inputstream.readline();
while (str!=null)
{
system.out.println(str);
str=inputstream.readline();
}
inputstream.close();
}
catch(exception e)
{
system.out.println(e.tostring());
}
}
public inputstream changetoy(inputstream inputstream)
{
try
{
datainputstream pipeout = new datainputsteam(inputstream);
pipedoutstream pipeout = new pipedoutputstream();
pipedlnsteam pipeln = new pipedlnputstream(pipeout);
printstream printstream = new printstream(pipeout);
ythread ythread = new ythread(xfileln,printstream);
ythread.start();
return pipeln;
}
catch(exeption e)
{
system.out.println(x.tostring());
}
return null;
}
public inputstream changetoz(inputstream inputsteam)
{
try
{
datainputstream yfileln = new datainputstream(inputstream);
pipeoutputstream pipeln2 = new pipedinputstream(pipeout2);
printrstream printstream2 = new printsteam(pipeout2);
zthread zthread = new zthread(yfileln,printstream2);
zthread.start();
return pipeln2;
}
catch(exception e)
{
system.out.println(e.tostring());
}
return null;
}
}
Ythread类和Zthread类
由于ythread类与zthread类基本一样,在此仅以ythread为例加以说明。
- 上一篇:java中的集合类
- 下一篇:Java用户界面编程指南(中文)2
精彩图集
精彩文章