Linux chmod命令详解和使用实例(改变文件或目录的访问权限)(2)
该命令有两种用法。一种是包含字母和操作符表达式的文字设定法;另一种是包含数字的数字设定法。
1). 文字设定法:
chmod [who] [+ | - | =] [mode] 文件名
2). 数字设定法
我们必须首先了解用数字表示的属性的含义:0表示没有权限,1表示可执行权限,2表示可写权限,4表示可读权限,然后将其相加。所以数字属性的格式应为3个从0到7的八进制数,其顺序是(u)(g)(o)。
例如,如果想让某个文件的属主有“读/写”二种权限,需要把4(可读)+2(可写)=6(读/写)。
数字设定法的一般形式为:
chmod [mode] 文件名
数字与字符对应关系如下:
r=4,w=2,x=1
若要rwx属性则4+2+1=7
若要rw-属性则4+2=6;
若要r-x属性则4+1=7。
4. 使用实例:
实例1:增加文件所有用户组可执行权限
命令:
chmod a+x log2012.log
输出:
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# chmod a+x log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
[root@localhost test]#
说明:
即设定文件log2012.log的属性为:文件属主(u) 增加执行权限;与文件属主同组用户(g) 增加执行权限;其他用户(o) 增加执行权限。
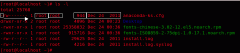
实例2:同时修改不同用户权限
命令:
输出:
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# chmod ug+w,o-x log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rwxrwxr-- 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
说明:
即设定文件text的属性为:文件属主(u) 增加写权限;与文件属主同组用户(g) 增加写权限;其他用户(o) 删除执行权限
实例3:删除文件权限
命令:
chmod a-x log2012.log
输出:
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rwxrwxr-- 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# chmod a-x log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
说明:
删除所有用户的可执行权限
实例4:使用“=”设置权限
命令:
chmod u=x log2012.log
输出:
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# chmod u=x log2012.log
[root@localhost test]# ls -al log2012.log
---xrw-r-- 1 root root 302108 11-13 06:03 log2012.log
说明:
撤销原来所有的权限,然后使拥有者具有可读权限
实例5:对一个目录及其子目录所有文件添加权限
命令:
输出:
[root@localhost test]# cd test4
[root@localhost test4]# ls -al
总计 312drwxrwxr-x 2 root root 4096 11-13 05:50 .
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 11-22 06:58 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 302108 11-12 22:54 log2012.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 61 11-12 22:54 log2013.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 11-12 22:54 log2014.log
[root@localhost test4]# cd ..
[root@localhost test]# chmod -R u+x test4
[root@localhost test]# cd test4
[root@localhost test4]# ls -al
总计 312drwxrwxr-x 2 root root 4096 11-13 05:50 .
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 11-22 06:58 ..
-rwxr--r-- 1 root root 302108 11-12 22:54 log2012.log
-rwxr--r-- 1 root root 61 11-12 22:54 log2013.log
-rwxr--r-- 1 root root 0 11-12 22:54 log2014.log
说明:
递归地给test4目录下所有文件和子目录的属主分配权限
其他一些实例:
1).
命令:
chmod 751 file
说明:
给file的属主分配读、写、执行(7)的权限,给file的所在组分配读、执行(5)的权限,给其他用户分配执行(1)的权限
2).
命令:
chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=x file
说明:
上例的另一种形式
3).
命令
chmod =r file
说明:
为所有用户分配读权限
3).
命令:
chmod 444 file
说明:
同上例
4).
命令:
chmod a-wx,a+r file
说明:
同上例