浅析Java语言中两种异常的差别[组图]
Java提供了两类主要的异常:runtime exception和checked exception。所有的checked exception是从java.lang.Exception类衍生出来的,而runtime exception则是从java.lang.RuntimeException或java.lang.Error类衍生出来的。
<!-- frame contents -->
一、机制上
它们在机制上的不同表现在两点:1.如何定义方法;2. 如何处理抛出的异常。请看下面CheckedException的定义:
public class CheckedException extends Exception
{
public CheckedException() {}
public CheckedException( String message )
{
super( message );
}
}
以及一个使用exception的例子:
public class ExceptionalClass
{
public void method1()
throws CheckedException
{
// ... throw new CheckedException( “...出错了“ );
}
public void method2( String arg )
{
if( arg == null )
{
throw new NullPointerException( “method2的参数arg是null!” );
}
}
public void method3() throws CheckedException
{
method1();
}
}
你可能已经注重到了,两个方法method1()和method2()都会抛出exception,可是只有method1()做了声明。另外,method3()本身并不会抛出exception,可是它却声明会抛出CheckedException。在向你解释之前,让我们先来看看这个类的main()方法:
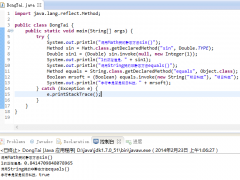
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ExceptionalClass example = new ExceptionalClass();
try
{
example.method1();
example.method3();
}
catch( CheckedException ex ) { } example.method2( null );
}
在main()方法中,假如要调用method1(),你必须把这个调用放在try/catch程序块当中,因为它会抛出Checked exception。
相比之下,当你调用method2()时,则不需要把它放在try/catch程序块当中,因为它会抛出的exception不是checked exception,而是runtime exception。会抛出runtime exception的方法在定义时不必声明它会抛出exception。
现在,让我们再来看看method3()。它调用了method1()却没有把这个调用放在try/catch程序块当中。它是通过声明它会抛出method1()会抛出的exception来避免这样做的。它没有捕捉这个exception,而是把它传递下去。实际上main()方法也可以这样做,通过声明它会抛出Checked exception来避免使用try/catch程序块(当然我们反对这种做法)。
小结一下:
* Runtime exceptions:
在定义方法时不需要声明会抛出runtime exception;
在调用这个方法时不需要捕捉这个runtime exception;
runtime exception是从java.lang.RuntimeException或java.lang.Error类衍生出来的。
* Checked exceptions:
定义方法时必须声明所有可能会抛出的checked exception;
在调用这个方法时,必须捕捉它的checked exception,不然就得把它的exception传递下去;
checked exception是从java.lang.Exception类衍生出来的。
二、逻辑上
从逻辑的角度来说,checked exceptions和runtime exception是有不同的使用目的的。checked exception用来指示一种调用方能够直接处理的异常情况。而runtime exception则用来指示一种调用方本身无法处理或恢复的程序错误。
- 上一篇:EJB 3.0开发指南之多表映射
- 下一篇:深入浅出Java设计之备忘录模式[组图]