利用Java实现串口全双工通讯
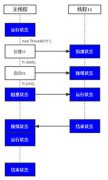
一个嵌入式系统通常需要通过串口与其主控系统进行全双工通讯,譬如一个流水线控制系统需要不断的接受从主控系统发送来的查询和控制信息,并将执行结果或查询结果发送回主控系统。本文介绍了一个简单的通过串口实现全双工通讯的Java类库,该类库大大的简化了对串口进行操作的过程。
本类库主要包括:SerialBean.java (与其他应用程序的接口), SerialBuffer.java(用来保存从串口所接收数据的缓冲区), ReadSerial.java (从串口读取数据的程序)。另外本类库还提供了一个例程SeriAlexample.java 作为示范。在下面的内容中将逐一对这几个部分进行具体介绍。
1. SerialBean
SerialBean是本类库与其他应用程序的接口。该类库中定义了SerialBean的构造方法以及初始化串口,从串口读取数据,往串口写入数据以及关闭串口的函数。具体介绍如下:
本函数构造一个指向特定串口的SerialBean,该串口由参数PortID所指定。PortID = 1 表示COM1,PortID = 2 表示COM2,由此类推。
public int Initialize()
本函数初始化所指定的串口并返回初始化结果。假如初始化成功返回1,否则返回-1。初始化的结果是该串口被SerialBean独占性使用,其参数被设置为9600, N, 8, 1。假如串口被成功初始化,则打开一个进程读取从串口传入的数据并将其保存在缓冲区中。
public String ReadPort(int Length)
本函数从串口(缓冲区)中读取指定长度的一个字符串。参数Length指定所返回字符串的长度。
public void WritePort(String Msg)
本函数向串口发送一个字符串。参数Msg是需要发送的字符串。
public void ClosePort()
本函数停止串口检测进程并关闭串口。
SerialBean的源代码如下:
package serial;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.comm.*;
/**
*
* This bean provides some basic functions to implement full dulplex
* information exchange through the srial port.
*
*/
public class SerialBean
{
static String PortName;
CommPortIdentifier portId;
SerialPort serialPort;
static OutputStream out;
static InputStream in;
SerialBuffer SB;
ReadSerial RT;
/**
*
* ConstrUCtor
*
* @param PortID the ID of the serial to be used. 1 for COM1,
* 2 for COM2, etc.
*
*/
public SerialBean(int PortID)
{
PortName = "COM" + PortID;
}
/**
*
* This function initialize the serial port for communication. It starts a
* thread which consistently monitors the serial port. Any signal captured
* from the serial port is stored into a buffer area.
*
*/
public int Initialize()
{
int InitSuccess = 1;
int InitFail = -1;
try
{
portId = CommPortIdentifier.getPortIdentifier(PortName);
try
{
serialPort = (SerialPort)
portId.open("Serial_Communication", 2000);
} catch (PortInUseException e)
{
return InitFail;
}
//Use InputStream in to read from the serial port, and OutputStream
//out to write to the serial port.
try
{
in = serialPort.getInputStream();
out = serialPort.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e)
{
return InitFail;
}
//Initialize the communication parameters to 9600, 8, 1, none.
try
{
serialPort.setSerialPortParams(9600,
SerialPort.DATABITS_8,
SerialPort.STOPBITS_1,
SerialPort.PARITY_NONE);
} catch (UnsupportedCommOperationException e)
{
return InitFail;
}
} catch (NoSuchPortException e)
{
return InitFail;
}
// when successfully open the serial port, create a new serial buffer,
// then create a thread that consistently accepts incoming signals from
// the serial port. Incoming signals are stored in the serial buffer.
SB = new SerialBuffer();
RT = new ReadSerial(SB, in);
RT.start();
// return success information
return InitSuccess;
}
/**
*
* This function returns a string with a certain length from the incoming
* messages.
*
* @param Length The length of the string to be returned.
*
*/
public String ReadPort(int Length)
{
String Msg;
Msg = SB.GetMsg(Length);
return Msg;
}
/**
*
* This function sends a message through the serial port.
*
* @param Msg The string to be sent.
*
*/
public void WritePort(String Msg)
{
int c;
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < Msg.length(); i++)
out.write(Msg.charAt(i));
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
/**
*
* This function closes the serial port in use.
*
*/
public void ClosePort()
{
RT.stop();
serialPort.close();
}
}
- 上一篇:用Java实现PDF报表
- 下一篇:Eclipse插件开发快速入门[图]