直接召唤系与IoCfashion使用Spring
Spring再强大,也要面对降临的问题--因为Spring不是Weblogic、Tomcat般的顶层容器,Servlet和EJB对象不由它创建,所以它必须要降临到Weblogic、Tomcat所在的位面。
初学者一般不用管那么多,照着Spring+hibernate+Struts之类的Sample就做了,但慢慢的,也许就要开始在jsp+Javabean体系,土制框架,Singleton类等环境下使用Spring了。
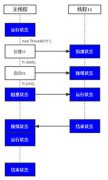
《Professional Java Development with the Spring Framework》第3章有"Managing the Containe"一节讲这个问题。一般可以分为直接召唤系与IoC fashion两类。
1.直接召唤系--Singleton的Application Context
最简单的,就像在UnitTest里那样,直接构造Application Context:
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClasspathXMLApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");
在Web环境里,会使用ContextLoader构造ApplicationContext后,压进Servlet Context。
由ContextLoaderListener或ContextLoaderServlet,在Web应用启动时完成。
然后在Jsp/Servelet中,可以通过Servlet Context取得ApplicationContext: ApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(application);
但像Singleton类或者EJB中,就没有Servlet Context可用了。
假如全部像UnitTest那样直接构造,速度就会很不堪。自然的,就想到把ApplicationContext做成单例。
Spring提供了ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator这样的物体。
先搞一个beanRefFactory.xml,里面写上所有的applcationContext-*.xml文件名,并把Context命名为"default-context": <beans>
<bean id="default-context" class="org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext">
<constrUCtor-arg>
<list> <value>applicationContext.xml</value></list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
然后让loactor去找它,但代码有点长: BeanFactoryReference bfr = DefaultLocatorFactory.getInstance().useBeanFactory("default-context");
BeanFactory factory = bfr.getFactory();
MyService myService = factory.getBean("myService");
bfr.release();
// now use myService
上面的代码实在是太灵活,太麻烦了。
还不如自己实现一个简单的Singleton,扩展ContextLoaderListener类,在Web系统启动时压入Singleton。
新的ContextLoaderListener类重载如下,ContextUtil中包含一个静态的ApplicationContext变量:
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event)
{
super.contextInitialized(event);
ServletContext context = event.getServletContext();
ApplicationContext ctx = WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext(context);
ContextUtil.setContext(ctx);
}
用家可直接取用:
ApplicationContext context = ContextUtil.getContext();