0. Preface: Core Technologies
0. Preface: Core Technologies
0.1 The Usual Suspects
This User Guide is written for active web developers and assumes a working knowledge about how Java web applications are built. Before getting started, you should understand the basics of several core technologies:
- HTTP, Html, and User Agents
- The HTTP Request/Response Cycle
- The Java Language and Application Frameworks
- JavaBeans
- Properties Files and ResourceBundles
- Java Servlets
- JavaServer Pages and jsp Tag Libraries
- Extensible Markup Language
This chapter briefly defines each of these technologies but does not describe them in detail. For your convenience, links to further information are provided if you would like to learn more about a technology.
If you are familiar with Java, but not these technologies, the best overall starting point is The Java Web Services Tutorial . This document is also available for download in PDF format.
If you've created web applications for other platforms, you may be able to follow along and visit the other references as needed. The core technologies used by Struts are also used by most other Java web development prodUCts, so the background information will be useful in any Java project.
If you are not familiar with the Java language generally, then the best starting point is The Java Tutorial . This overlaps with the Java Web Services Tutorial in some places, but the two work well together.
For more about building Java application in general, see the New to Java tutorial.
0.2 HTTP, HTML and User Agents
The World Wide Web was built over the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). A User Agent, like a web browser, uses HTTP to request a HTML document. The browser then formats and displays the document to its user. HTTP is used to transport more than HTML, but HTML is the lingua franca of the Web and web applications.
While building web applications, some Java developers will write their own HTML. Others leave that responsibility to the page designers.
For more about HTTP, HTML, and User Agents, see:
- Getting started with HTML by Dave Raggett
- HTTP Overview in the Java Web Services Tutorial.
- HTTP/1.1 Specification
- HTTP Basic and Digest Authentication Specification
- State Management Mechanism Specification (Cookies)
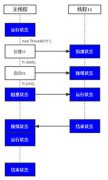
0.3 The HTTP Request/Response cycle
- 上一篇:有关松散耦合与接口的使用
- 下一篇:Table of Contents 目录