C++中的类型转换static_cast、dynamic_cast、const_cast和reinterpret_cas(2)
但是,在类A和类B中必须包含虚函数,为什么呢?因为类中存在虚函数,就说明它有想让基类指针或引用指向派生类对象的情况,此时转换才有意义;由于运行时类型检查需要运行时类型信息,而这个信息存储在类的虚函数表中,只有定义了虚函数的类才有虚函数表。
4.如果expression是type-id的基类,使用dynamic_cast进行转换时,在运行时就会检查expression是否真正的指向一个type-id类型的对象,如果是,则能进行正确的转换,获得对应的值;否则返回NULL,如果是引用,则在运行时就会抛出异常;例如:
class B
{
virtual void f(){};
};
class D : public B
{
virtual void f(){};
};
void main()
{
B* pb = new D; // unclear but ok
B* pb2 = new B;
D* pd = dynamic_cast<D*>(pb); // ok: pb actually points to a D
D* pd2 = dynamic_cast<D*>(pb2); // pb2 points to a B not a D, now pd2 is NULL
}
这个就是下行转换,从基类指针转换到派生类指针。
对于一些复杂的继承关系来说,使用dynamic_cast进行转换是存在一些陷阱的;比如,有如下的一个结构:

D类型可以安全的转换成B和C类型,但是D类型要是直接转换成A类型呢?
class A
{
virtual void Func() = 0;
};
class B : public A
{
void Func(){};
};
class C : public A
{
void Func(){};
};
class D : public B, public C
{
void Func(){}
};
int main()
{
D *pD = new D;
A *pA = dynamic_cast<A *>(pD); // You will get a pA which is NULL
}
如果进行上面的直接转,你将会得到一个NULL的pA指针;这是因为,B和C都继承了A,并且都实现了虚函数Func,导致在进行转换时,无法进行抉择应该向哪个A进行转换。正确的做法是:
int main()
{
D *pD = new D;
B *pB = dynamic_cast<B *>(pD);
A *pA = dynamic_cast<A *>(pB);
}
这就是我在实现QueryInterface时,得到IUnknown的指针时,使用的是*ppv = static_cast<IX *>(this);而不是*ppv = static_cast<IUnknown *>(this);
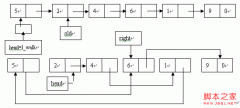
对于多重继承的情况,从派生类往父类的父类进行转时,需要特别注意;比如有下面这种情况:

现在,你拥有一个A类型的指针,它指向E实例,如何获得B类型的指针,指向E实例呢?如果直接进行转的话,就会出现编译器出现分歧,不知道是走E->C->B,还是走E->D->B。对于这种情况,我们就必须先将A类型的指针进行下行转换,获得E类型的指针,然后,在指定一条正确的路线进行上行转换。
上面就是对于dynamic_cast转换的一些细节知识点,特别是对于多重继承的情况,在实际项目中,很容易出现问题。
const_cast
const_cast的转换格式:const_cast <type-id> (expression)
const_cast用来将类型的const、volatile和__unaligned属性移除。常量指针被转换成非常量指针,并且仍然指向原来的对象;常量引用被转换成非常量引用,并且仍然引用原来的对象。看以下的代码例子:
/*
** FileName : ConstCastDemo
** Author : Jelly Young
** Date : 2013/12/27
** Description : More information, please go to http://www.jb51.net
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CA
{
public:
CA():m_iA(10){}
int m_iA;
};
int main()
{
const CA *pA = new CA;
// pA->m_iA = 100; // Error
CA *pB = const_cast<CA *>(pA);
pB->m_iA = 100;
// Now the pA and the pB points to the same object
cout<<pA->m_iA<<endl;
cout<<pB->m_iA<<endl;
const CA &a = *pA;
// a.m_iA = 200; // Error
CA &b = const_cast<CA &>(a);
pB->m_iA = 200;
// Now the a and the b reference to the same object
cout<<b.m_iA<<endl;
cout<<a.m_iA<<endl;
}
注:你不能直接对非指针和非引用的变量使用const_cast操作符去直接移除它的const、volatile和__unaligned属性。
reinterpret_cast
reinterpret_cast的转换格式:reinterpret_cast <type-id> (expression)