谈谈TCP和UDP的一些简单应用
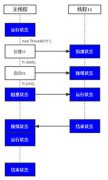
网络最基本的精神就是让两台机器连接起来,“被呼叫的一方”也就是服务器,而“找人的一方”则叫做客户机,所以说在连接中服务器、客户机也就是一个相对的概念了。而我们对机器的标识主要是通过IP地址和端口来区分的。
“传输控制协议”TCP和“用户数据报协议”是两种不同的协议,JAVA对这两种协议的支持基本是一致的,而它们本身最大的区别也就是发送的可靠性和速率,前者相比后者是可靠协议,后者当然是速度快得多了,下面我们分别用两个SOCKET下演示:
eg1:
//Clients.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class Clients
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getByName(null);
Socket socket = new Socket(addr,2000);
PrintWriter out =
new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
socket.getOutputStream())),true);
byte[] b = new byte[2048];
String msg = new String(b,0,System.in.read(b));
out.println(msg);
socket.close();
}
}
//Servers.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class Servers
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
ServerSocket s = new ServerSocket(2000);
try{
while(true){
Socket socket = s.accept();
try{
BufferedReader in =
new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int c;
while( (c = in.read()) != -1 ){
char ch = (char)c;
sb.append(ch);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}catch(IOException e){
socket.close();
}finally{
socket.close();
}
}//while
}finally{
s.close();
}//try
}//main
}
此程式主要用Servers来进行无限监听,而Clients是客户机发送程式,他们的端口全采用2000。
eg2:
//UDPsend.java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
/**
* This class sends the specified text or file as a datagram to the
* specified port of the specified host.
**/
public class UDPSend {
public static final String usage =
"Usage: java UDPSend ...
" +
" or: java UDPSend -f ";
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
// Check the number of arguments
if (args.length < 3)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong number of args");
// Parse the arguments
String host = args[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
// Figure out the message to send.
// If the third argument is -f, then send the contents of the file
// specified as the fourth argument. Otherwise, concatenate the
// third and all remaining arguments and send that.
byte[] message;
if (args[2].equals("-f")) {
File f = new File(args[3]);
int len = (int)f.length(); // figure out how big the file is
message = new byte[len]; // create a buffer big enough